Digital is just not a word anymore;its your life. Part and parcel of humans, economy, and countries. Each country is trying to regulate, innovate, implement digital solutions, services and lifestyles. Today we are going to discuss about one such beautiful country Jordan and the evolutions of mobile wallets in the stunning landscape. What kind of consumers in Jordan may benefit from mobile money? Is the government in Jordan supportive enough of digital wallets? How do the refugees in Jordan get aid via mobile financial services? All of this and lot more in our post of today on Jordan and its mobile wallets.
Understanding Jordan’s Population and Economy
Jordan, officially known as The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is an Arab country uniquely situated at the crossroads of three continents: Asia, Africa, and Europe. Connecting East to West, Jordan has been a key trading post in the Middle East for centuries. As Wikipedia says – Jordan is classified as an upper-middle-income country, and in 2010 Jordan was ranked as the most globalized country in the Middle East and North Africa region. Also, as per IMF Jordan’s banking sector is classified as “highly developed.”
But what does the number says? The below diagram represents the population and economy of Jordan as per Jan 2019. With ~91% of the urban population and 98% of literacy rate, indeed Jordan could be termed as a literate country.
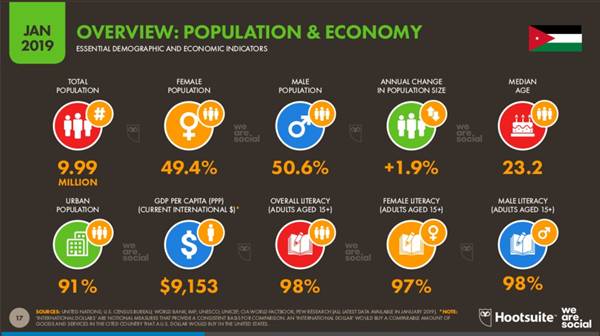
In the late 1990s, the Jordanian government adopted the goal of developing an intellectually competitive IT industry, one that attracts both foreign and local investments, generating high-value jobs, and producing substantial levels of export. In particular, aggressive initiatives have been taken to implement Internet-based technologies to help facilitate the desired social and economic development. So what happened to the efforts applied in the ’90s?
The below diagram shows the stats of users in Jordan that have a mobile subscription, use internet, social media and social media via mobile phones.

https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2019-jordan
And the below diagram represents the annual digital growth i.e., the year-on-year change in key statistical indicators

The interesting point is that although Mobile subscriptions have seen a decline, the increase in population is almost equal to the change in mobile social media users. Could we say that Mobile with an active internet/data connection is on the rise in Jordan?
Here is another diagram highlighting the number of internet users; it is worth noting that of the total 87% of internet users, 81% use internet on mobile.

Another data set specifically on Mobile Data plan says out of 80% of mobile connections, 79% are using 3G/4G.

So, my hypothesis that Mobile with an active internet/data connection is on the rise in Jordan seems true. But unfortunately, the mobile and data plan is not being used efficiently, and there is a lack of financial inclusion, bill payments and mode of payment for shopping is still cash. The below diagram shows the stats in detail.
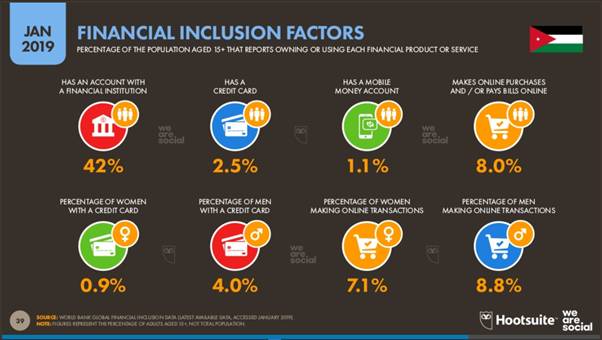
Its really shocking to know that Jordan, a country that has a literacy rate of almost 98%, where 80% of users can afford a smartphone and a 3G/4G connection, only 42% have a bank account, and only 8% has made an online purchase.
Do you think using the mobile + 3G/4G penetration the above numbers could be improved? I certainly believe that the tiny handset connected to the internet has the power to change the dynamics of a nation. Let’s explore the use cases of a mobile wallet in Jordan –
Opportunities for Mobile Industry in Jordan
Influx of Refugees
As of August 2019, Jordan hosts over 660,000 Syrian refugees – around 48% of them children. The vast majority (about 80%) live in urban areas, while the remainder resides mainly in two refugee camps. The influx of refugees leads to high population growth and opens opportunities’ for business growth, given the current mobile penetration rate.
The high percentage of youth
Almost 70% of the total population in Jordan is under 30 years of age, and people between the age of 15 and 24 years is nearly 22%, making a majority population of youth in the country. Being tech-savvy and early adopters of technology, mobile penetration is at its peak in the nation.
Emerging networks and services
The fixed broadband network is growing with the national broadband network fiber-based deployment well underway. Firms like Orange Jordan launched 4G+ services in 2018, and there are talks of IoT [Internet of Things] making their way in Jordan homes and businesses.
Where Can Banks Pitch In with their Mobile Financial Services in Jordan
Robust Infrastructure and Push from Regulatory Authorities
Jordan has a sound regulatory environment and working on numerous on-going initiatives –
- The Central Bank of Jordan released a circular on mobile payments in 2010 and published a regulatory framework in December 2013 for mobile money, which went into effect on March 2014.
- In 2016 the Central Bank of Jordan issued a Mobile Payment Service Operational Framework that clarifies the structure of processes, techniques, limits, and operational environment of the mobile phone payment service.
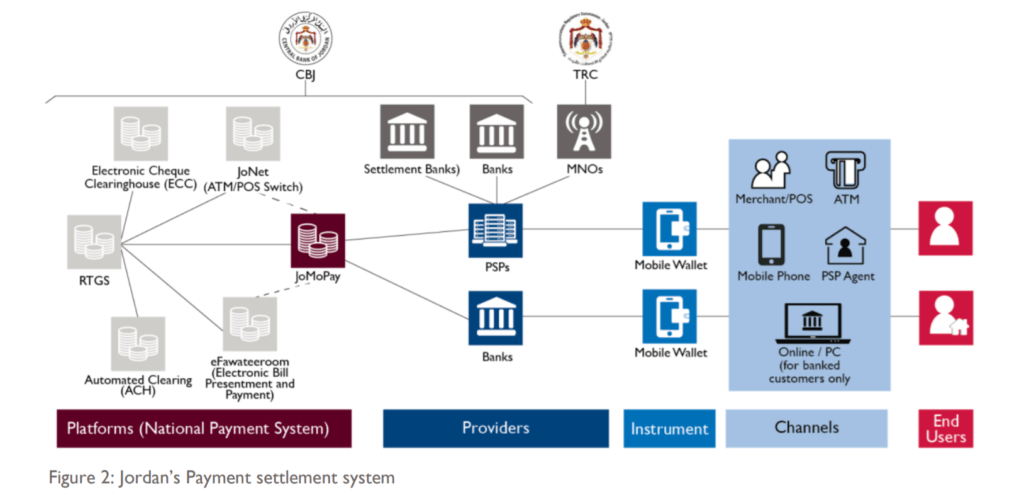
- As shown in the diagram below the Payment infrastructure of Jordan is robust and highly developed for banks, NBFC’s and PSP’s [Payment Service Provider] to support domestic and international payments.
- The Mobile Infrastructure offers a reliable and robust broadband network at an affordable price, also equipped with nationwide wireless access. As per data presented in the report Tanmey Ahjo it indicates that internet and mobile phone coverage were above 100% by 2017. Even the # of computers in every household was 55.8%, and internet access at home was 55.8%, and individuals using internet were 66.8%.
Driving Innovations via Technology for Rural and remote Customers
Although mobile money solutions or e-wallet solutions are available in the Kingdom, they are majorly concentrated in urban regions and dominated by traditional players such as Post Offices, Banks ATM’s or Exchange Houses. Fintech and startups could target the rural and remote areas with their innovative mobile-based solutions to get penetration and visibility.
Targeting Refugees
Jordan hosts the second-highest ratio of refugees in the world. A significant portion of these refugees are women and children, with more than 80 percent living below the poverty line. As of October 2018, of the total 8,000 Syrian refugees have registered for mobile wallets with payment service providers. Though thesenumbers areimpressive, while comparing with the total population of over 600,000 Syrian refugees in Jordan, it is quite small. Also, the wallet’s usage is shallow due to low funds and lack of trust in the digital ecosystem. Another concern that accounts for low usage is refugees do not receive the “aid” onto their wallets adding an extra step for individuals to deposit aids in their wallet account and then use them.
The startups, Fintech’s and Banks could use this an opportunity and propose innovative solutions like a system that directly credits the aid onto individuals’ wallet account for government benefits. Also developing an agent network within themselves would help Banks and FI’s to earn trust
Supporting the Agent Network or Solopreneurs
According to the Central Bank of Jordan stats of July 2018, there were 1,409 agents in the market. The Agents serve as the bridge between a Payment Service Provider [PSP] and individuals to avail banking services and get revenues. However, the report highlights some concerns and doubtsabout the effectiveness of an Agent network in Jordan with issues like agent network not well-regulated and specific to a geography.
These issues can be taken up with digitization by providing an Agent Banking Solution that could help these foot soldier’s in digitizing cash-in and cash-outs, also assist them with imparting financial education to the individuals and lastly aids in automatic reconciliation at the end of the day.
Streamlining onboarding and eKYC
The KYC norms in Jordan vary with each bank/Financial institution like JoMoPay has designed their onboarding process for a new customer such that if he is a resident, he can provide his national ID number (for Jordanian citizens), for foreigners their passport number, for refuges, their UN [HCR ID] number, or the number of their Ministry of Interior (MOI) service card. But all of this is a manual process.
Onboarding of a customer should be automated and seamless, so while Central Bank of Jordan is working on an e-KYC system linking it to the biometric signature, it needs to cater to various needs of ID’s carried by customers.
Mobile phones and the internet are game-changers of an economy. And there is a huge opportunity to accelerate inclusiveness without the need for additional investment in infrastructure. A mobile wallet is not only a solution for wide variety of individuals in Jordan but also serve businesses, SME’s, B2B and government organization in digitizing payments and finances.
If you are looking to deploy a mobile wallet solution in Jordan and need a technology provider, we are just a call away.